What is material handling?
In supply chain management, material handling is a far-reaching concept that includes various types of equipment and activities. It occurs whenever a material or product is being moved from one place to another – be it within the same department, in two separate buildings, or between a building and a transportation vehicle.
However, material handling involves much more than a short-distance movement of products or materials. By definition, it refers to the science and art of protecting, storing, and controlling products and materials throughout their manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, consumption, and disposal.
Material handling can be considered as one of the most critical activities within an organization. Poor material handling can have sweeping consequences on production flow, employee safety, and warehouse management. Therefore, in order to improve warehouse operations, it is crucial that organizations are acquainted with all optimization solutions available.
Material handling equipment
To make industrial processes more economical, various types of material handling equipment and machinery are used. These come in all shapes and sizes, performing a range of functions crucial for the processes of your business.
Depending on production requirements, the market offers a wide variety of manual, semi-automatic, and automatic material handling equipment and machinery. Examples of the most commonly used material handling equipment include:
- Monorail systems and workstation cranes
- Lift trucks
- Overhead cranes
- Conveyors
- Automatic guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs)
- Industrial robots
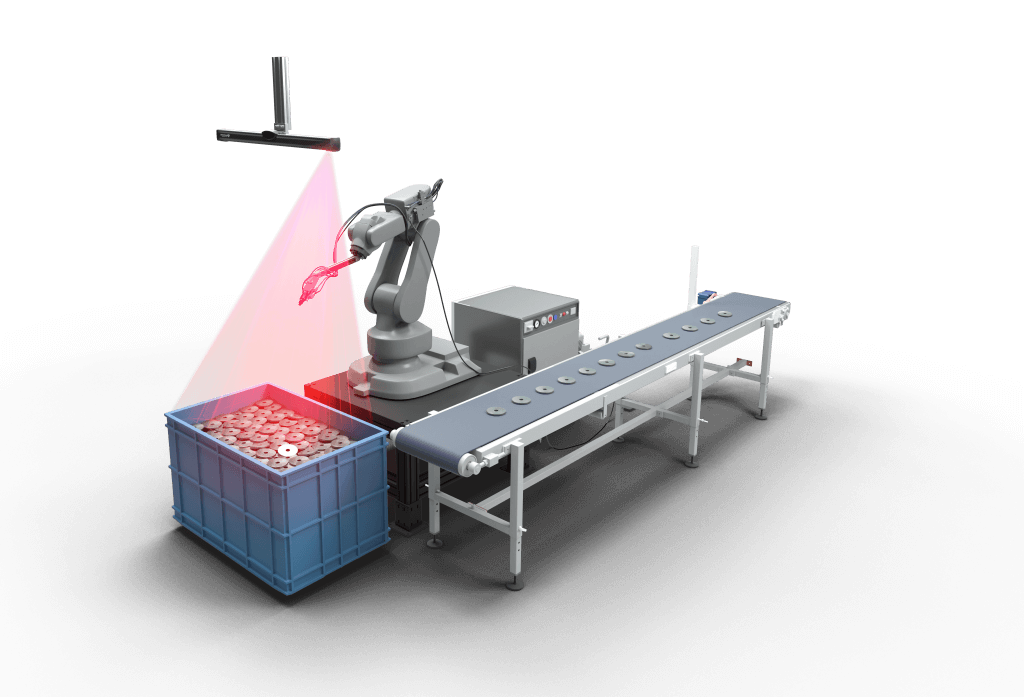
Automation in material handling
In the old times, due to the lack of efficient technology available, all material handling activities were done manually. Workers used their hands to lift, carry, and transfer materials and products within a warehouse or a building. However, manual material handling often requires a lot of strenuous physical labor, increasing the chances of workplace accidents and slowing down production processes.
The increasing manufacturing and logistical requirements combined with rapid technology enhancements have led to the development of various types of material handling solutions that respond to different budgets and needs. Businesses around the world are taking advantage of semi-automated and automated material handling systems that can bring immense benefits to operational efficiency.
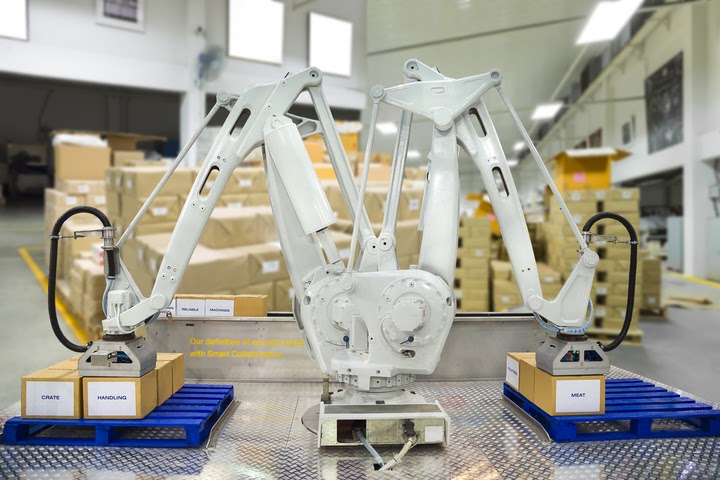

In automated material handling, robots and other advanced computerized devices are used to move, lift, store, or retrieve products and materials. In this type of material handling, all tasks are performed by automation equipment. Workers, on the other hand, are only required to oversee and control the processes done by machinery. The automation of material handling, therefore, plays an important role in reducing the risks of workplace accidents, among other benefits.
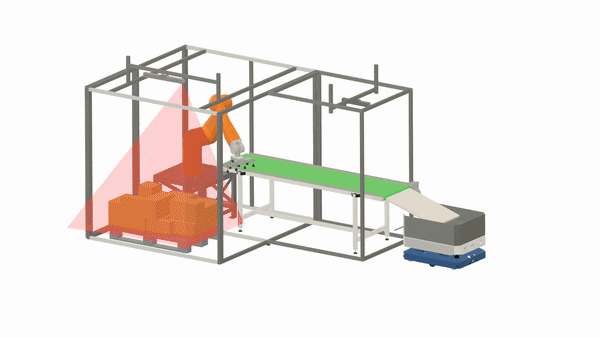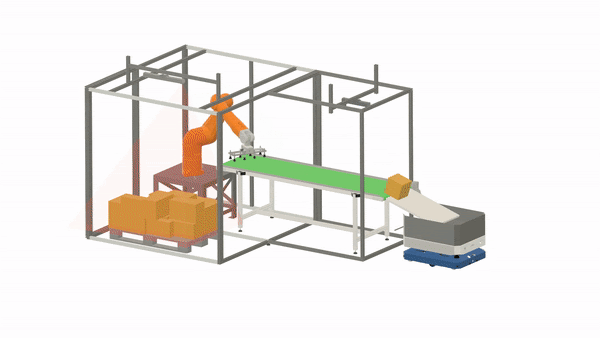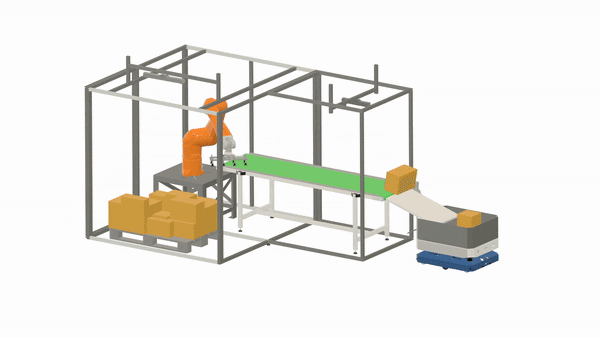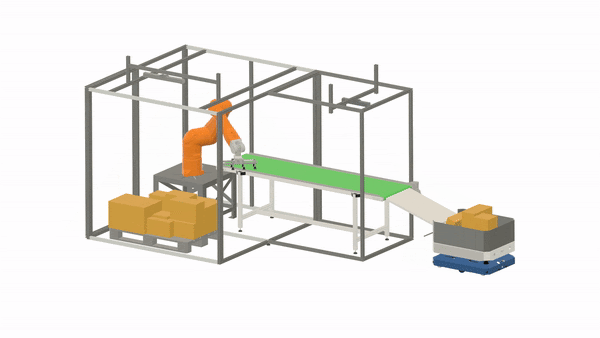
Some material handling solutions are only semi-automated, as they still require a human operator to perform tasks that are too costly or difficult to fully automate, such as loading and driving. However, with the advancements in robotics and robot intelligence, an increasing number of material handling tasks can already be handled without human intervention.
The role of automation in material handling
Automated material handling is performed by automated material handling systems (AMHS), often referred to as automated material transport systems (AMTS) and automated transport systems (ATS). They use robots and computerized devices to move, pull, push, lift, or store materials and products, significantly reducing or eliminating the need for human intervention.
AMHSs may consist of single mechanical equipment or a set of various machines. Examples of AMHSs include conveyors, stackers, industrial lifting devices and equipment box lifts, bins, and trolleys, among others.
AMHSs use item tracking and carrier systems to detect materials or goods and their location, route the items based on the material identifier, and then transport them. The identification of items is achieved through the use of various carrier and material tracking systems, such as optical character recognition, barcoding, and radio-frequency identification.
Benefits of automation in material handling
We have already touched upon some of the most important benefits of automated material handling. However, the benefits the automation of material handling offers are much broader. Here are some of the most important advantages of adopting AMHSs in your business:
- Automation reduces the risk of workplace accidents: Employee safety is among the top concerns of businesses in the industrial sector. Manual material handling often includes physical activities such as heavy materials lifting, bending, and twisting, which may result in minor or serious injuries. Automation reduces the amount of physical material handling activities and the direct intervention of workers, which minimizes the risks of workplace accidents.
Photoneo universal depalletization system, for instance, can pick boxes weighing up to 50 kg, which are often placed a few meters above the ground. The automation of unloading pallets therefore significantly reduces the risk of back injuries and other health detriments.
- Automation improves efficiency: Thanks to automation, workers are able to complete their tasks more easily and efficiently, which speeds up the overall manufacturing process. Also, taking advantage of an AMHS reduces the chances of human error – for instance, eliminating manual list checking significantly improving inventory management.
Another fact is that a robot can work non-stop, without ever getting tired, which also reduces the risk of human errors caused by fatigue and monotonous tasks. Photoneo AI-powered automation solutions can unload 1000 boxes or singulate and sort 2,250 parcels within one hour – a rate which could never be achieved by manual operation.
- Automation improves quality control: Automated material handling involves also automated quality control processes and inspections. Automated machines detect more errors and thus reduce the need for rework and the chances of waste production. An AMHS makes manufacturing processes more precise and therefore improves product quality.
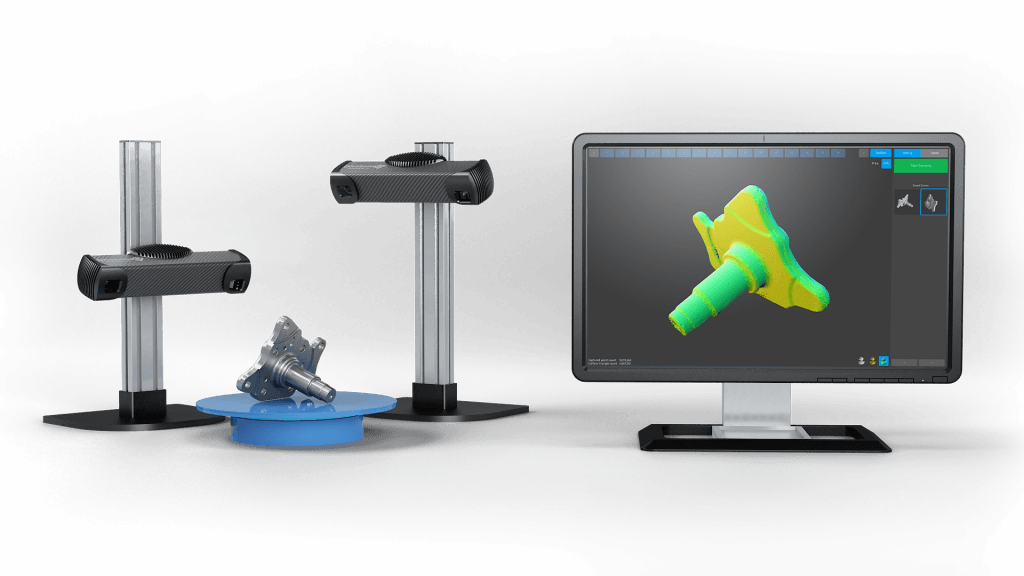
The PhoXi 3D Scanner from Photoneo, for instance, provides a high level of detail with a resolution of 3,2 Million 3D points and an accuracy of 25 – 500 um across the different models. When combined with the PhoXi 3D Meshing system for a high-quality creation of 3D models, it presents an ideal tool for quality control, inspection, and metrology – an automation system that readily outperforms human vision and manual inspection.
- Automation saves money: Even though the initial investment in the implementation of an AMHS is rather high, it will gradually translate into significant cost savings. Automated material handling requires fewer people involved in the processes, reducing overall personnel expenses.
- Automation makes data access more efficient: Prior to automation in material handling, the individual pieces of equipment and work areas within an industrial setting worked in isolation. Connected automation systems enable facility managers, logistics experts, and other employees to access all important data whenever they need. Additionally, since robots communicate with each other, they have the ability to react to surrounding conditions, reducing picking times and risks of injuries.
- Automation maximizes space: Thanks to automated systems such as lifts, materials and products can be stored higher and accessed more easily, which makes the use of space more economical. This frees additional storage space and workspace in the plant or warehouse.
The deployment of automation systems also requires less floor space compared to the number of workers required for the manual operation of a workstation. This in turn leads to another cost savings.
Conclusion
Manufacturers are constantly under pressure to do things cheaper, faster, but also better in terms of quality. The profitability and productivity of a distribution center or a warehouse are largely influenced by the efficiency and reliability of its material handling activities. Therefore, material handling plays a crucial role within every company’s production and supply chain processes.
Thanks to various automated material handling solutions, companies can significantly improve their customer’s operations and company profitability. Moreover, applying the right AMHSs enables considerable cost savings, while also increasing the overall workplace safety and production efficiency.
Since every warehouse is unique, it also requires a unique solution that matches its needs. If you consider improving your current material handling solution, we are here to answer any questions you might have considering the automation of your warehouse.


