Automated robotic system for post-construction quality assessment
Partner:
Challenge:
Post-construction quality assessment of buildings is an indispensable procedure in the construction industry, currently executed manually by inspectors. According to the building and construction authority (BCA) of Singapore, which is responsible for the manual assessment of all buildings in Singapore, at least two inspectors are needed to complete the manual procedures in a standard daily quality inspection operation. One uses manual assessment tools and the other one prepares reports. The manual assessment procedure may lead to several errors caused by executing the operation in an incorrect way or using inaccurate inspection tools. The inspector may also get tired and the inspection accuracy may decrease over time. In addition, the manual inspection is usually done during daytime.
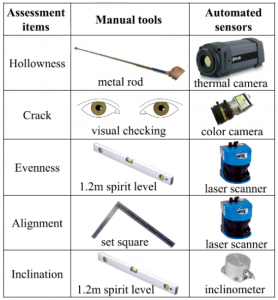
The customer proposed an automated post-construction quality assessment robotic system capable of simultaneously assessing five types of defects – hollowness, cracks, evenness, alignment and inclination. These represent 80% of common defects found during the construction quality assessment.
Solution:
The robotic system consists of a mobile robot, 2D laser scanner, colour camera, thermal camera with a heater and an inclinometer.
Images and point clouds are used to check evenness and cracks on the construction wall.
Discussion:
The high-accuracy measurement is able to cover a large area without complicated and bulky rotating mechanism – alternative for a laser scanner.
The automated solution reduces the amount of labour by approximately 50%. The costs for assessing and surveying construction sites are reduced by 30%, based on market surveys and robot performance.
Would you like to know more about Photoneo technology and how it can benefit your applications?