Machine Vision Systems: From Industry Applications to Cost Implications
Various machine vision systems each offer unique advantages for automating tasks. From simple inspections to complex robotic guidance, let’s explore the key differences between these technologies and their fit for your industry, desired application, or budget. We’ll help you make an informed, clarity-driven decision, backed by real-world examples and key ROI implications.
Machine Vision Systems: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Both the 2D and 3D machine vision systems markets are poised for substantial growth, with a projected annual growth rate of 12.3% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. This expansion highlights the increasing demand for automated vision solutions across various industries.
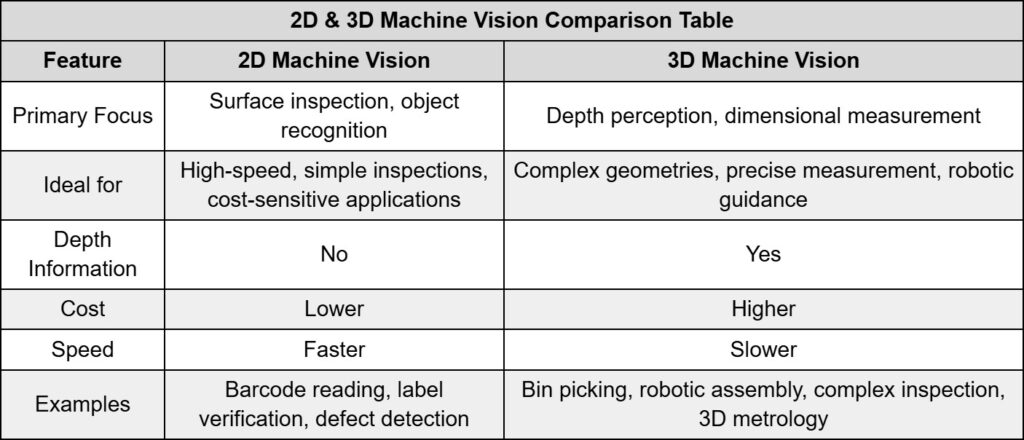
While both 2D and 3D machine vision systems play crucial roles in industrial automation, they have distinct capabilities and applications. 2D vision systems excel at analyzing images based on color, shape, and texture, making them effective for tasks like quality inspection, object recognition, and code reading.
3D vision systems, on the other hand, capture and analyze three-dimensional data, enabling depth perception and spatial understanding. This allows for accurate measurements, complex object recognition, and vision-guided robotics.
How do 2D and 3D vision systems work?
In 2D vision, key capabilities are achieved using conventional cameras to capture two-dimensional images, which are then processed by specialized software. 2D systems are known for their speed and efficiency, making them suitable for high-throughput applications like manufacturing, automotive, and healthcare industries.
In fact, quality checks and inspections represent the largest share of the 2D vision systems market, accounting for 51.84% in 2022. They are also cost-effective compared to 3D systems and relatively simple to implement and maintain. However, 2D systems lack depth perception, limiting their use in applications requiring spatial understanding. They can also be sensitive to lighting variations and environmental factors.
3D vision systems, however, employ technologies like laser scanners, structured light, or stereo vision to generate 3D point clouds or depth maps. The advantages of this technology include providing accurate dimensional measurements and volumetric analysis. They are also robust to lighting changes and environmental variations, enabling complex tasks like bin picking, robotic guidance, digital twinning, and 3D modeling.
This makes them particularly valuable in industries like robotics, logistics, and manufacturing, where precise measurements of size, volume, and distance are critical. Any drawbacks? 3D systems are generally more expensive than 2D systems and can be more complex to implement, often requiring specialized expertise.
Ideal applications for 2D and 3D machine vision systems
Did you know the machine vision market size is expected to explode in the next few years? We’re talking about a $41 billion market by 2030, growing steadily at around 12% each year. Now that we have the global growth overview, let’s delve into the best-fitting applications of 2D and 3D vision systems for your next application.
Choosing the right machine vision system for industrial automation depends on your needs. Here’s a breakdown of when 2D and 3D systems excel.
2D Machine Vision Applications
2D machine vision finds ideal applications in analyzing surfaces and identifying objects based on their appearance.
- Surface flaws: Detecting scratches, dents, or discoloration on products like electronics, car parts, and packaging.
- Object sorting: Identifying and sorting items by their visual characteristics (e.g., shape, color, label) in logistics and manufacturing.
- Barcode scanning: Quickly and accurately codes and QR codes for tracking and inventory management.
- Simple presence/absence: Checking if a component is present on a production line for quality control.
- Fast-paced production: Efficiently inspecting items on high-speed production lines due to rapid image capture and processing.
3D Machine Vision Applications
More complex, 3D machine vision provides depth information, making it suitable for applications needing precise measurements and spatial understanding.
- Accurate measurements: Obtaining precise dimensions and analyzing the shape of objects in industries like aerospace and precision engineering.
- Shape and volume analysis: Assessing the completeness and accuracy of 3D objects like molded parts or machined components.
- Robot guidance: Guiding robots for pick-and-place tasks by providing accurate object location and orientation.
- Bin picking: Enabling robots to pick objects from unorganized bins using depth perception.
- Assembly verification: Ensuring precise component placement and alignment during assembly processes.
Cost Comparison of Machine Vision Systems
When evaluating machine vision systems, understanding the cost implications is essential for making informed decisions. Both 2D and 3D vision systems have a broad price range, influenced by their complexity, features, and intended applications. Here’s a detailed look at the cost comparisons between the two.
General Price Considerations
Initial investment plays a crucial role in decision-making. 2D systems generally have a lower entry point, making them more accessible for companies with limited budgets, while 3D systems require a higher initial investment, especially for mid-range and high-end options. Long-term value is another factor; while 2D systems can be more affordable upfront, they may lack the versatility and depth of analysis that 3D systems offer, potentially limiting their long-term applications.
Conversely, 3D systems, although pricier, can lead to increased efficiency and improved quality control, making the investment worthwhile in demanding environments. Additionally, operational costs for both systems include maintenance, software updates, and training, but 3D systems may incur higher costs due to their sophisticated setup and calibration requirements.

2D Vision Systems
- Entry-Level Systems: Priced between $200 to $3,000, these systems are suitable for basic applications like simple quality checks or barcode reading, offering standard resolution and basic software capabilities.
- Mid-Range Systems: Ranging from $3,000 to $10,000, these systems provide better resolution and faster processing speeds, making them ideal for more complex industrial applications that require higher precision.
- High-End Systems: Costing $10,000 to over $25,000, these advanced systems feature ultra-high-resolution cameras and sophisticated software suites, designed for high-speed automation lines and intricate assembly checks.
3D Vision Systems
- Entry-Level Systems: Starting at $3,000 to $10,000, these systems are intended for straightforward tasks like basic measurements and inspections, offering standard resolution and speed.
- Mid-Range Systems: Priced between $10,000 and $30,000, these systems deliver higher resolution and processing power, suitable for detailed inspections and precise robot guidance.
- High-End Systems: These systems can range from $30,000 to over $60,000, featuring top-of-the-line resolution and rapid processing capabilities for complex applications, such as high-speed robot guidance and precision metrology.
Industries Where 3D Machine Vision Systems Prove The Most Cost-Effective
As we can see, while much more powerful and versatile, 3D vision systems can cost considerably. However, 3D vision systems are becoming increasingly vital across various industries because they enhance efficiency, improve product quality, and reduce costs. Here’s a look at some key sectors where they are making a significant impact.
Automotive Industry
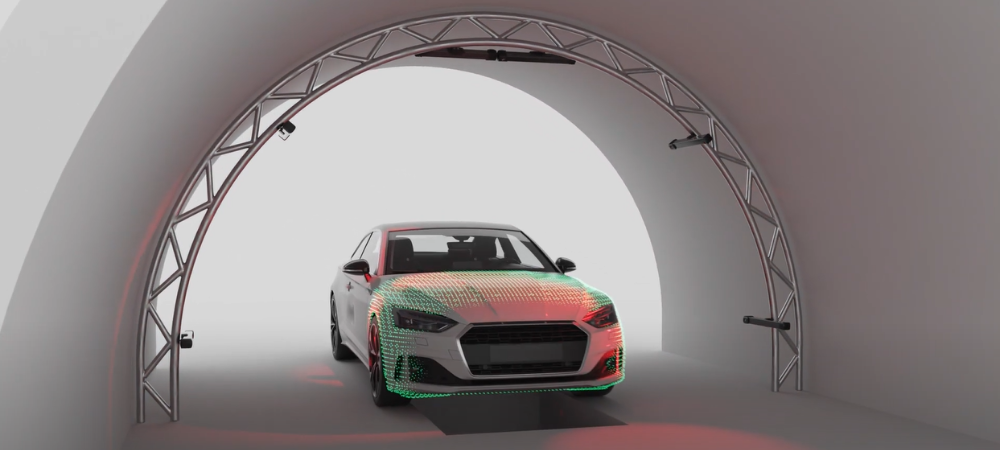

3D vision systems are essential for accurately aligning and assembling complex car parts. They help in detecting defects and ensuring that components fit together correctly, which is crucial for quality control in automotive manufacturing. These systems enable robots to navigate dynamic environments effectively, facilitating tasks like picking and placing components with high accuracy, thus improving overall production efficiency.
Automating this field with 3D vision can also count on a viable return on investment due to global market projections. According to the Interact Analysis report, the automotive industry, the largest consumer of machine vision products, experienced significant growth in 2023, particularly in Germany. This high demand helped offset potential losses in machine vision revenue, making 2023 a reasonable year for the sector despite pandemic-related challenges like supply chain disruptions and semiconductor shortages.
Driven by a 12.3% growth in Germany and a 4.9% rise in the US, the automotive market contributed to a 5.02% growth in machine vision for the automotive sector (MIO Automotive) in the previous year.
Electronics and Semiconductors Inspection
The technology ensures high-quality standards are met by enabling detailed quality inspections of delicate components like semiconductor wafers. This leads to reduced waste and improved yield rates. This sector is expected to grow rapidly in 3D vision adoption due to the increasing demand for high-quality manufacturing.
Notably, the semiconductor industry is experiencing unprecedented growth, fueled by the demand for increasingly powerful and intelligent devices. This growth is not only reflected in the volume of chips produced but also in t heir complexity, making the manufacturing process more challenging than ever. To ensure the quality and efficiency of these intricate chips, manufacturers are relying on advanced inspection tools, with 3D vision emerging as a key technology.
According to the World Semiconductor Trade Statistics, the global semiconductor market is experiencing a strong rebound, growing by 16% in 2024, which totals a $611 billion market value. This positive outlook is driven by a better-than-expected performance in recent months, particularly in the computing sector. Looking further ahead, WSTS anticipates continued growth in 2025, with the market reaching $687 billion, a 12.5% increase.
Healthcare & Medical Sector
A fresh runner-up among automation-adopting industries is healthcare. However, though enhanced vision systems that revolutionize diagnostics or even aim to automate certain surgical tasks might come as a no-brainer, there’s much more to medical applications of 3D vision systems. Just think of all the medical products and items. Most of them come packaged in transparent plastic bags.
An issue? Shiny and transparent objects have been virtually invisible to 3D sensors and cameras.
The root of the problem lies in the unique optical properties. Light passes directly through transparent objects, while glossy surfaces scatter and reflect light erratically. This makes it extremely difficult to accurately capture their surface geometry for 3D reconstruction.
Traditional workarounds, like repositioning the scanner or coating the object with special substances, proved impractical and often ineffective in real-world applications. Therefore we pushed the boundaries of MotionCam-3D, capturing what was once invisible – transparent objects.
Manufacturing and Logistics
3D vision systems enhance product quality through precise measurements and defect detection. In logistics, they enable robots to navigate complex environments, improving automation and efficiency. This ultimately leads to lower operational costs and increased productivity.
Especially logistics is going through a revolution in automation. In 2023, the logistics automation market was worth $65.25 billion, and by 2033, it’s projected to skyrocket to an astounding $217.26 billion. That means it’s expected to grow at a rate of 12.8% each year. Essentially, businesses are rapidly adopting automation to streamline their logistics operations, making them faster, more efficient, and more cost-effective. And there are good reasons for that.
3D vision systems are transforming logistics by bringing significant benefits to a range of applications. These systems enhance efficiency by automating tasks like package sorting and palletizing, reducing manual labor, and improving speed.
They also increase accuracy in picking and placing items, minimizing errors and damages. By providing precise measurements, 3D vision enables optimized container loading and efficient use of space. This technology also enhances safety by improving obstacle detection and navigation for robots in warehouse environments.
Conclusion
Ultimately, whether you need to consider a 3D vision system or you’re good with 2D cameras depends mainly on your application and the industry you operate in. While high-quality 2D cameras can bring outstanding results in simpler applications at a more affordable price, 3D cameras can prove vital in automation-ready industries, in more challenging applications, demanding vision-guided robotics that recognize space and depth.
Want to take a deeper dive into machine vision and in-depth comparisons of 2D and 3D systems? Download our free e-book to learn more!
.png)


